First Home Savings Account (FHSA): What You Need to Know
The First Home Savings Account (FHSA) is a savings plan designed for first-time home buyers in Canada, which allows them to save up to $40,000 tax-free. Contributions to an FHSA are tax-deductible, similar to Registered Retirement Savings Plans (RRSP). Additionally, income and gains earned inside the account and withdrawals are tax-free, like a Tax-Free Savings Account (TFSA).
In this article and accompanying infographic, we will provide you with the necessary information you need to know about FHSA, including eligibility requirements, contributions and deductions, income and gains, qualifying investments, withdrawals, and transfers.
Eligibility Requirements
To be able to open an FHSA, you need to meet all the following eligibility requirements:
- Residency: You must be an individual who is a resident of Canada.
- Age: You must be at least 18 and not reach 72 in the current year.
- First-time Home Buyer: You must be a first-time home buyer, which means that neither you nor your spouse had owned a qualifying home that was your principal residence at any point during the calendar year or the preceding four calendar years before the account was opened.
Contributions and Deductions
There are limits to the amount you can contribute to your FHSA.
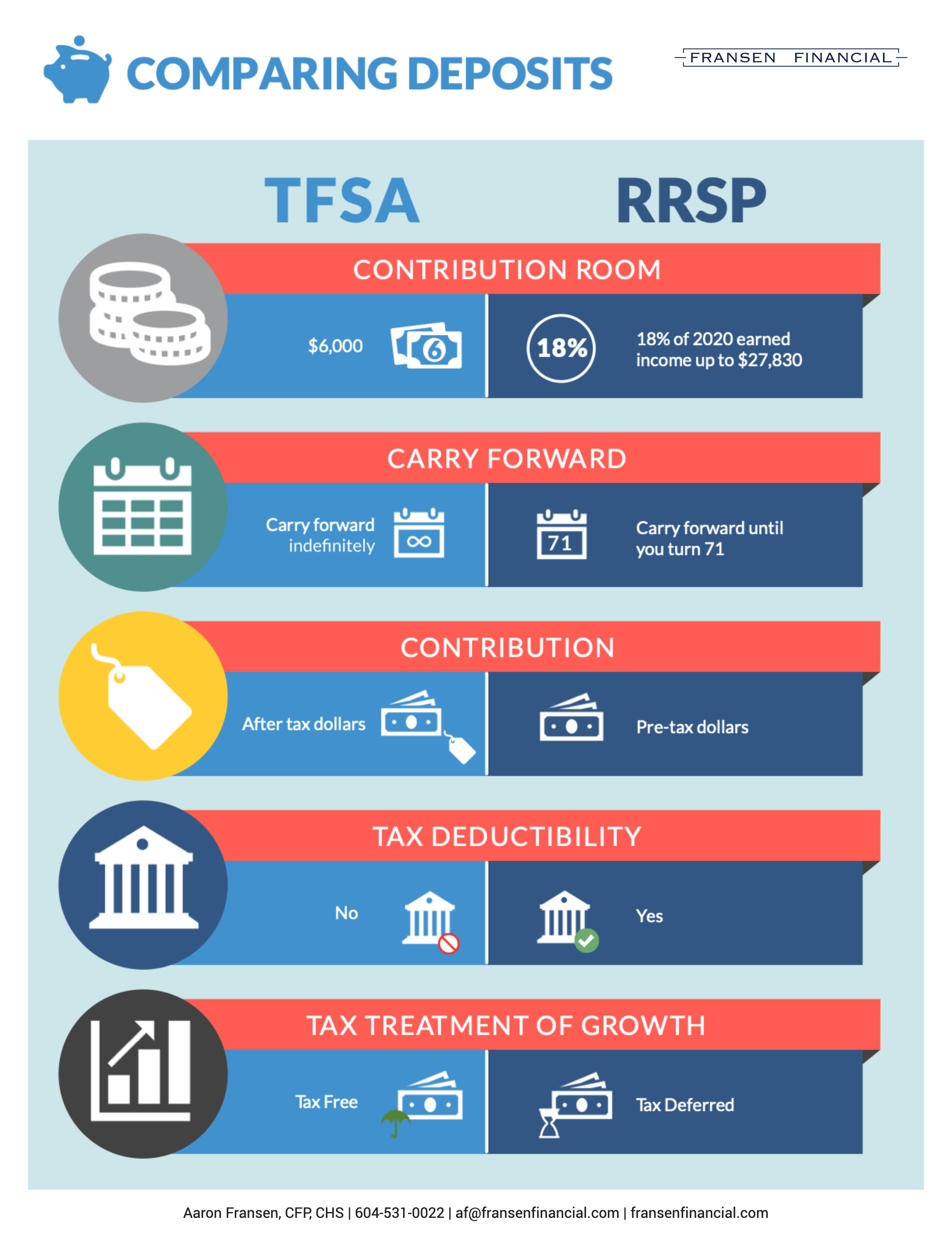
- The annual contribution limit is $8,000.
- The lifetime contribution limit is $40,000.
If you do not contribute the full amount each year, the contribution room carries forward to the following year. However, carry-forward amounts only start accumulating after you open an FHSA for the first time, and they do not automatically begin when you turn 18.
Any excess contributions are subject to a penalty of 1% per month.
Tax Deductions
By claiming contributions made to FHSA accounts as a deduction against all taxable income sources, the amount of taxable income for the year can be reduced, resulting in a decrease in the amount of taxes payable.
Suppose you choose not to claim the FHSA deduction in the year. In that case, you can carry forward the unused contribution amounts indefinitely and claim them as a deduction later, like RRSP deductions.
Qualifying Investments
Qualifying investments for an FHSA are like those allowed in RRSPs and TFSAs, including mutual funds, segregated funds, ETFs, stocks, bonds, and GICs.
Incomes and Gains
The income and capital gains earned in an FHSA are not included in your annual income for tax purposes and therefore are not deductible. This means that the investment can continue to grow and compound within the FHSA tax-free like a TFSA.
Qualifying Withdrawals
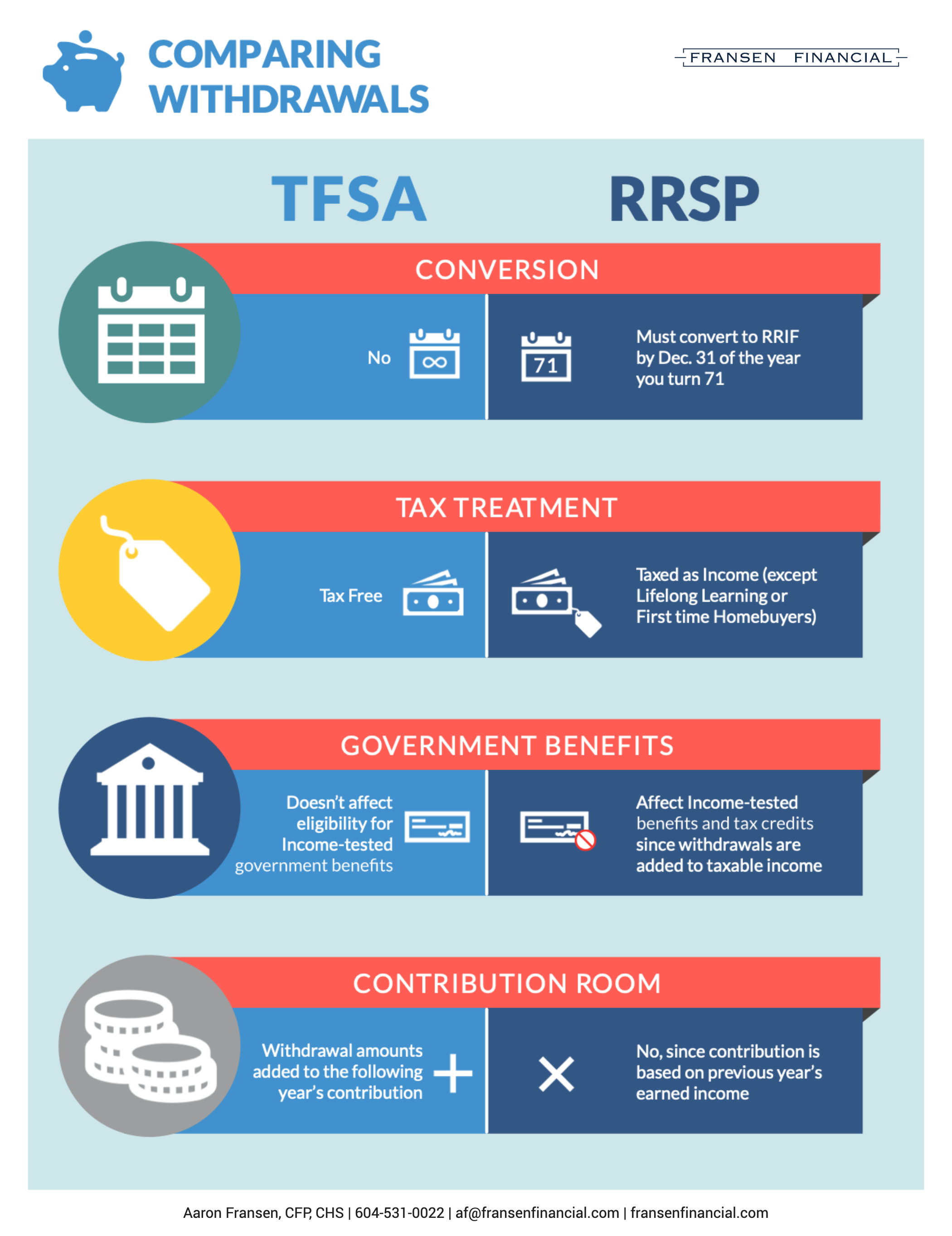
Withdrawals from an FHSA are subject to specific rules and conditions. Qualifying withdrawals made to purchase a home are tax-free but must meet specific criteria:
- The person making the withdrawal must be a first-time home buyer and a Canadian resident.
- They must also intend to use the property as their primary residence within one year of purchasing or building it.
- The home being purchased must be in Canada, and a written agreement to buy or build the home must be in place before October 1st of the year following the withdrawal.
It is not possible to restore FHSA contribution limits by making withdrawals or transfers.
Transfers
Unused funds in an FHSA account following a qualifying withdrawal can be transferred tax-free to an RRSP or Registered Retirement Income Fund (RRIF) until the end of the following year from the year of the first withdrawal. Transfers do not affect the available RRSP contribution room, but the transferred funds will be taxable when withdrawn from the account.
It’s important to remember that there are limitations on how long you can keep your FHSA account. You must close your FHSA after you’ve held it for 15 years or by the end of the year in which you turn 71, whichever comes first.
If you’re considering opening an FHSA or saving for a home, we can help; contact us.
Mutual Funds and Segregated Funds provided by the Fund Companies are offered through Worldsource Financial Management Inc., sponsoring mutual fund dealer. Other Products and Services are offered through Fransen Financial Inc.